Studies in s indicate that brown adipose tissue is important in the regulation of body weight, and it is possible that individual variation in adaptive thermogenesis can be attributed to variations in the amount or activity of brown adipose tissue. Until recently, the presence of brown adipose
Energy ingested as fat beyond that needed for current energy demands is stored in adipose tissue. In addition, carbohydrate and protein consumed in the diet can be converted to fat.
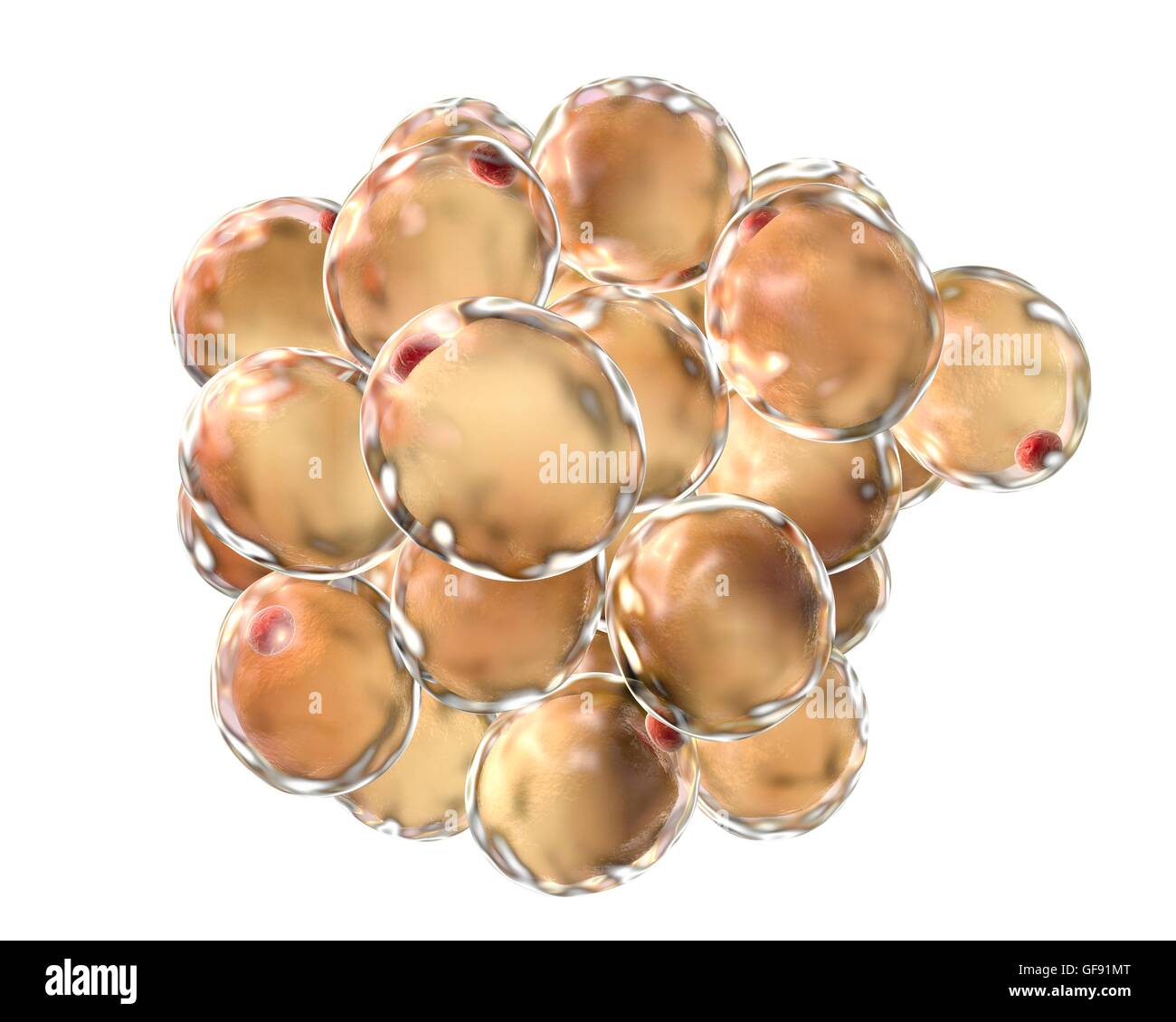

Adipose cell: Adipose cell, connective-tissue cell specialized to synthesize and contain large globules of fat. There are two types of adipose cells: white adipose cells contain large fat droplets, only a small amount of cytoplasm, and flattened, noncentrally located nuclei; and brown adipose cells contain fat
Within a couple of months, he was convinced adipose stem cells, found in abdominal fat, may be something that could finally provide lasting relief for his aching back. — dr. sanjay gupta and roni selig, CNN, “Jack Nicklaus’ secret stem cell therapy: ‘I didn’t keep it private; no one asked me about it’,” 27 Apr. 2018
Adipose tissue (body fat) is crucial for health. Along with fat cells, adipose tissue contains numerous nerve cells and blood vessels, storing and releasing energy to fuel the body and releasing important hormones vital to the body’s needs.

Brown adipose tissue (BAT) or brown fat makes up the adipose organ together with white adipose tissue (or white fat). Brown adipose tissue …

The adipose tissue page provides a discussion of the role of this tissue in overall metabolic regulation, fat storage, and inflammatory processes.
In biology, adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells and a variety of immune cells such as adipose tissue macrophages.
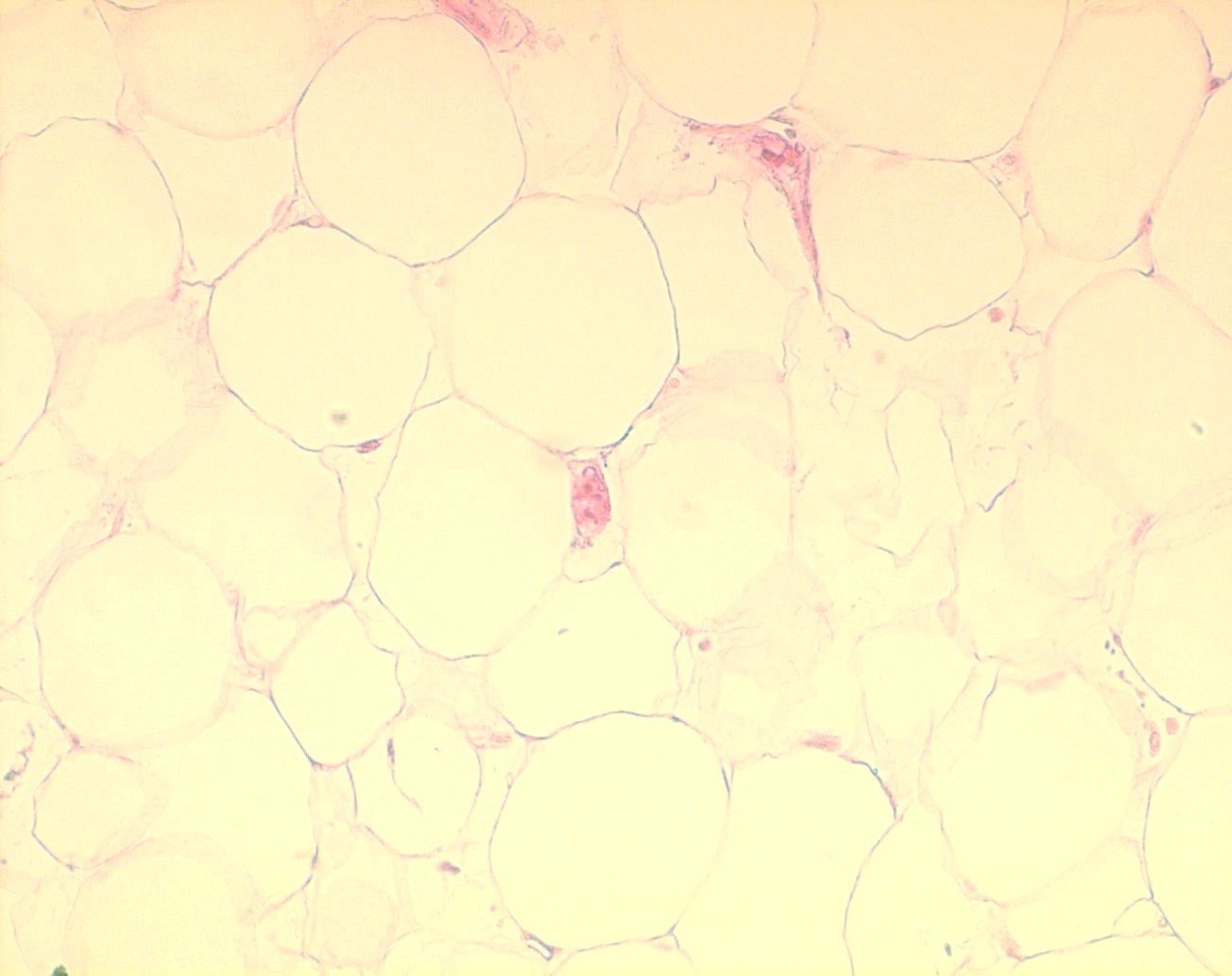

Obesity results from an imbalance between energy intake and expenditure. 1,2 The adipose-tissue pool in mammals is composed of at least two functionally different types of fat: white and brown.
Adipose tissue, or fat, is an anatomical term for loose connective tissue composed of adipocytes. Its main role is to store energy in the form of fat, although it also cushions and insulates the body.


