
Adult stem cells are undifferentiated cells found throughout the body that divide to replenish dying cells and regenerate damaged tissues. Also known as somatic stem cells, they can be found in ren, as well as adults.

Benefits of Stem Cells to Human Patients Adult Stem Cells v. Embryonic Stem Cells Download This List Peer-Reviewed References (not a complete listing, sample references) Adult Stem Cells Embryonic Stem Cells Cancers: Brain Cancer Retinoblastoma Ovarian Cancer Skin Cancer: Merkel Cell Carcinoma Testicular Cancer Tumors

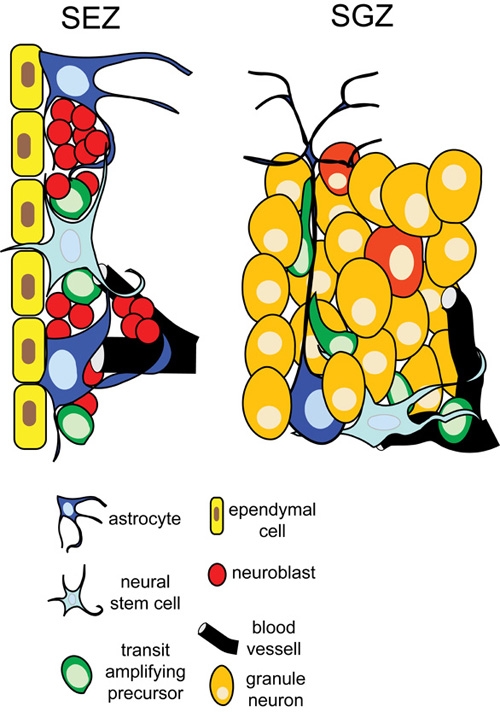
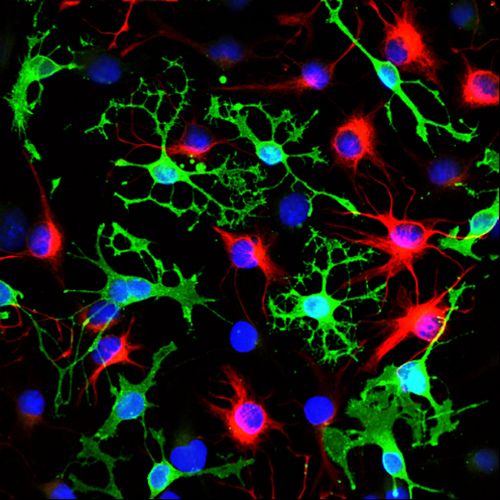
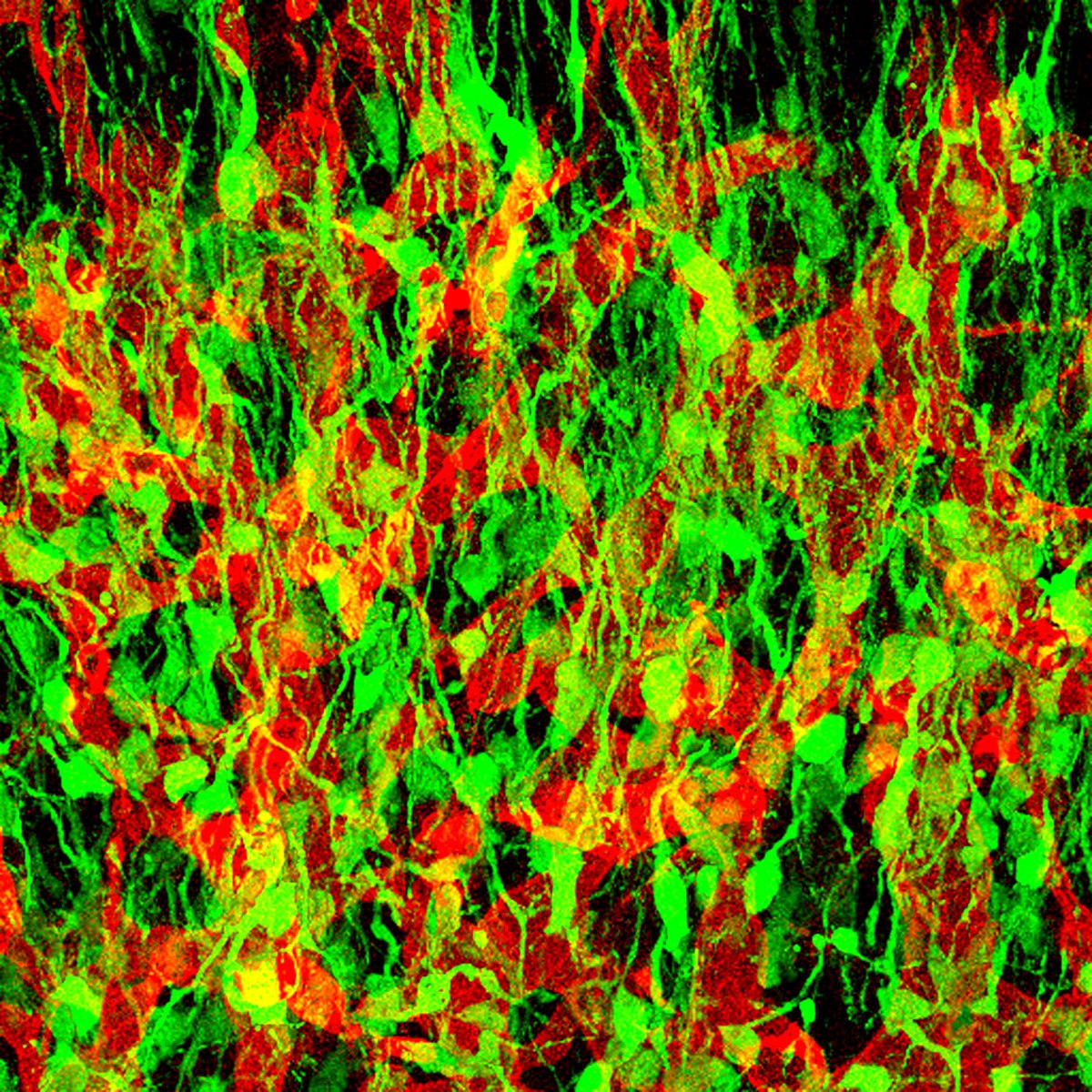
Neural stem cell: Neural stem cell, largely undifferentiated cell originating in the central nervous system. Neural stem cells (NSCs) have the potential to give rise to offspring cells that grow and differentiate into neurons and glial cells (non-neuronal cells that insulate neurons and enhance the speed at which
Neural stem cells (NSCs) are self-renewing, multipotent cells that generate the neurons and glia of the nervous system of all s during embryonic development.Some neural stem cells persist in the adult vertebrate brain and …
Adult Stem Cell Treatment is a natural solution to treat a variety of medical diseases and conditions. Learn about it’s positive impact on our site.
Stem cell research and applications in the treatment of diseases like Retinitis Pigmentosis, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, Spinal Cord Injury, Retinal Degeneration. Home of SallyTemple’s lab.
Search for articles by this author Affiliations. Department of Stem Cell Biology, Institute for Frontier Medical Sciences, Kyoto University, Kyoto 606-8507, Japan
Adult stem cells (or Somatic Stem Cell): Stem cells that are harvested from tissues in an adult body. These cells are usually multipotent, meaning they can differentiate into cells from some, but not all, of the three germ layers.

Transmission electron micrograph of an adult stem cell displaying typical ultrastructural characteristics.


Cell Stem Cell publishes peer-reviewed articles reporting findings of unusual significance in all areas of stem cell research, including biological advances and …
